class iii malocclusion slideshare
The embrasure between the lower canine and the lower first premolar is shifted forward with regard to the upper canine blue arrows. If it does not grow vertically there is an indirect effect on the mandiblewhich then rotates upward and forward as it grows producing an appearance of mandibular prognathism that.
3-5 UK -IN ASIAN POPULATION.
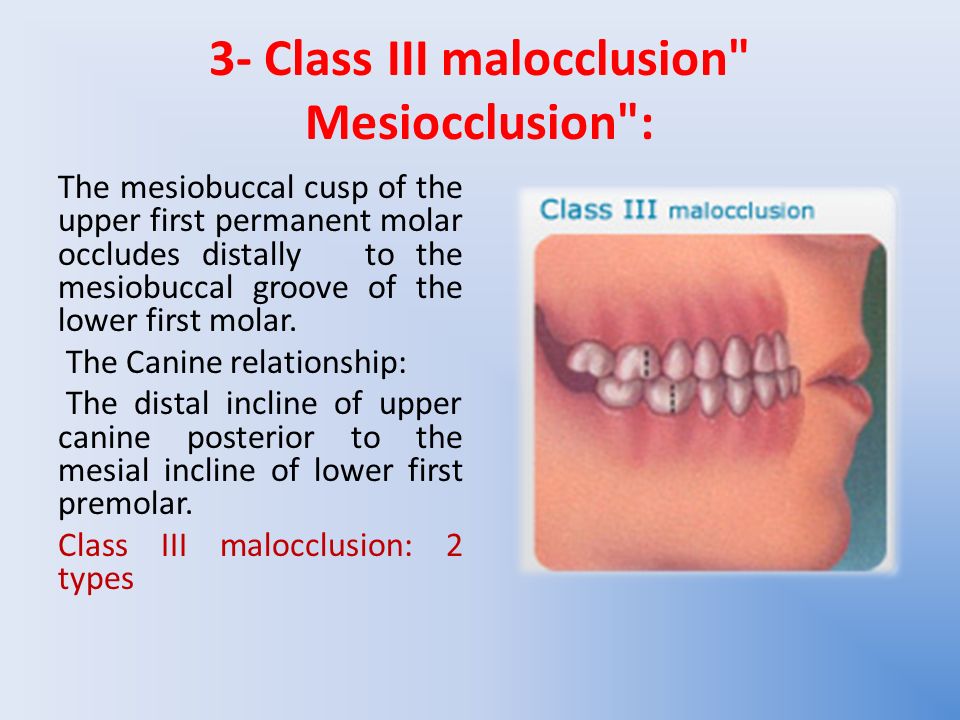
. Is purely dental due to different axial inclination of UL anterior teeth or one of them OJ0-1-2 mm2. In cases of mandibular prognathism the jaw is developed by excess in relation to the maxilla and the inferior dental arch extends forward beyond the superior causing a Class III malocclusion also known as underbite. The Amount of Growth in subjects with Class III Malocclusion is significantly different than in subjects with normal occlusion unfavorable 2.
Prevalence of class III malocclusion in Caucasians ranges from 08 to 40 and rises up to 1213 in Chinese and Japanese populations while in North Indian population class III malocclusion is found in up to 34 of the population. 10 IN CHILDREN 4. Clinically Class III malocclusion is in two forms.
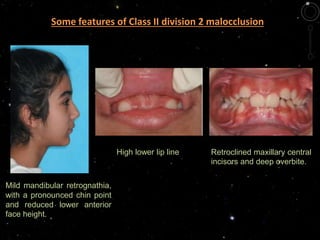
Class II malocclusion with deep bite was described by Strang as a condition with overlapping of the upper anterior teeth over the lowers in the vertical plane. Incisor superocclusion 2 mesiodistal tooth size 3 molar infraocclusion 4 vertical maxillary over growth 5. VTs GROWTH IN PATIENTS WITH CLASS IIIGROWTH IN PATIENTS WITH CLASS III MALOCCLUSIONSMALOCCLUSIONS The craniofacial skeletal pattern of children with ClassThe craniofacial skeletal pattern of children with Class III malocclusion is evident in the early deciduousIII malocclusion is evident in the early deciduous dentitiondentition.
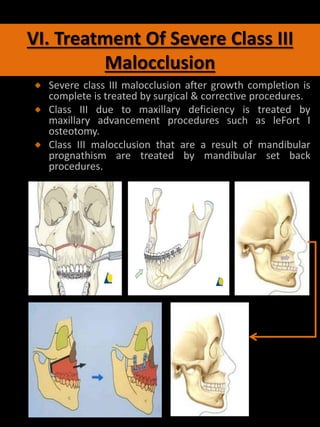
In subjects with Class III Malocclusion the Peak in Mandibular Growth occurs later in development and lasts longer than. PSEUDO CLASS III MALOCCLUSION Due to occlusal prematurity when the mandible moves from rest position to occlusion it slides forward into a pseudo class III position. After surgical correction of the skeletal discrepancy the occlusion is usually finished orthodontically to a Class I relationship.
She had significant anteroposterior and transverse discrepancies a concave profile and strained lip closure. Class II malocclusion. A pseudo or functional Class III due to an early interference with the muscular reflex of mandibular closure and b the true Class III.
This is a pseudo-Class III malocclusion 5. The center of the lower first molar mesiobuccal groove is anterior to. CLASS III SUB-DIVISION Condition in which class III molar relationship is present only on one side with normal relation on the other side.
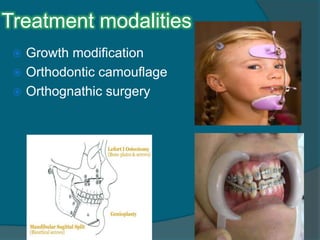
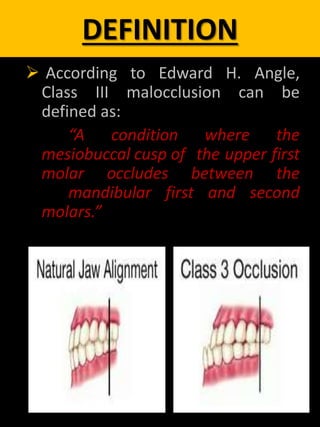
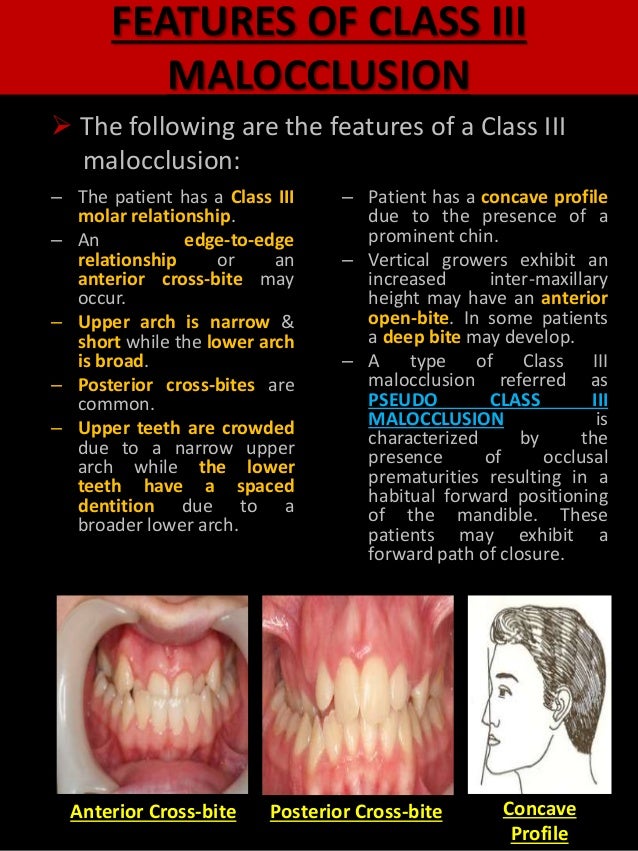
Get ideas for your own presentations. Surgical treatment of Class III malocclusion includes in most cases mandibular retrusion maxillary protrusion or a combination of both. In Class III malocclusion the overjet is reduced and may be reversed with one or more incisor teeth in lingual crossbite.
Treatment of adult patients with Class III malocclusion might require orthognathic surgery especially when the deformity is severe with a significant impact on facial esthetics. The aim of the present case report is to describe the orthodontic-surgical treatment of a 17-year-and-9-month-old female patient with a Class III malocclusion poor facial esthetics and mandibular and chin protrusion. It may be caused by many conditions ie.
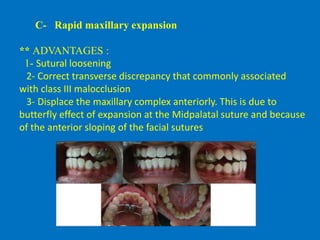
Maxillary deficiency Both anteroposterior and vertical maxillary deficiency can contribute to Class III malocclusion. If the maxilla is small or positioned posteriorly the effect is direct. Typical Presentation OF Class 3 Malocclusion 6.
Sometimes a Class III relationship is caused by a forward shift of the mandible to avoid incisal interferences. View Class 3 Malocclusion PPTs online safely and virus-free. -Class III incisor.
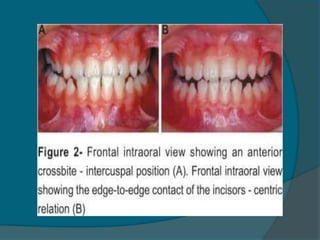
In which the cause of the reverse OJ. The mandible and mandibular incisors are then guided anteriorly in central occlusion resulting in an anterior crossbite. 50 Generally as growth is completed there is little or no functional shift of the mandible on closure.
Class III malocclusion is considered to be one of the most difficult and complex orthodontic problems to treat. The American Veterinary Dental College defines Class II malocclusion as mandibular distocclusion when there is an abnormal rostro-caudal relationship between the dental arches in which the mandibular arch occludes caudal to its normal position relative to the maxillary arch Figure 3Terms that have commonly been associated with class II. Learn new and interesting things.
However adult patients with an anterior crossbite should still check for functional shift CO-CR discrepancy during clinical. Is when the lower incisor edge lies anterior to the cingulum plateau of the upper incisors. In the early mixed dentition and in older patients with mild skeletal.
It is where an anterior displacement masking an underlying sk class I base. Class III molar relationship exists on one side. Class III A class III intermaxillary relationship means that the lower teeth are shifted forward with regard to the upper teeth.
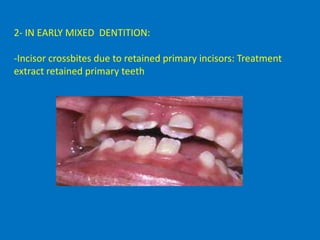
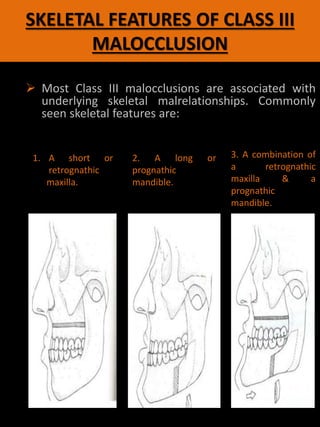
Forward movement of the mandible during jaw closure can also result from premature loss of deciduous posterior teeth. Impacted teeth can remarkably influence treatment planning which should be precise and concise to allow a reasonably short treatment time with low biologic cost. Skeletal Class III malocclusion can be classified into retruded maxilla protruded mandible or a combination of the two according to cephalometric analysis.
Class III malocclusions are the least common type of malocclusion yet they are often more complicated to treat and more likely to require orthognathic surgery for optimal correction. Pseudo Class III Malocclusion Pseudo class III malocclusion is a habitual established cross bite of all anterior teeth without any skeletal discrepancy resulting from functional forward positioningshift of the mandible on closure. Many classifications of severity of class III had been reviewed the accepted one as follow- 1mild CL III dental.
1 The reported incidence of this malocclusion ranges between 1 to 19 with the lowest among the Caucasian populations 23 and the highest among the Asian populations. Its also known as postural class III. Intraorally she had a negative overjet.
Class III skeletal malocclusion with a prognatic jaw is one of the most serious maxillofacial deformities although it is important to underline that this is considered a. Class III Malocclusion is not helping at all. PSEUDO Class III malocclusion FALSE or postural which occurs when mandible shifts anteriorly during final stages of closure due to premature contact of incisors or the canines.
Mandibular clockwise rotation can also provide the same result as mandibular retrusion when increase. Share yours for free. May be attributed partly to jaws and the other part to teeth.
Moderate CLIII dento-skeletal. The etiology of Class III malocclusion is multifactorial with genetic ethnic environmental and habitual components. A sample of 69.
Anterior crossbite with functional shift also called pseudo Class III is a malocclusion in which the incisal edges of one or more maxillary incisors occlude with the incisal edges of the mandibular incisors in centric relationship.
100 Malocclusions Common Orthodontic Problem Mohamad Aboualnaser Awat
Orthodontic Dr Enas Talb 4th Class Ppt Video Online Download

Classification Of Orthodontic Malocclusion Ppt Download

Class Iii Malocclusion Ppt Download